#06 - Learning Experience Design
a design disclipline
The organisational unit Educational Technology supports you in creating successful digital learning environments; its development is influenced by the LXD discipline.
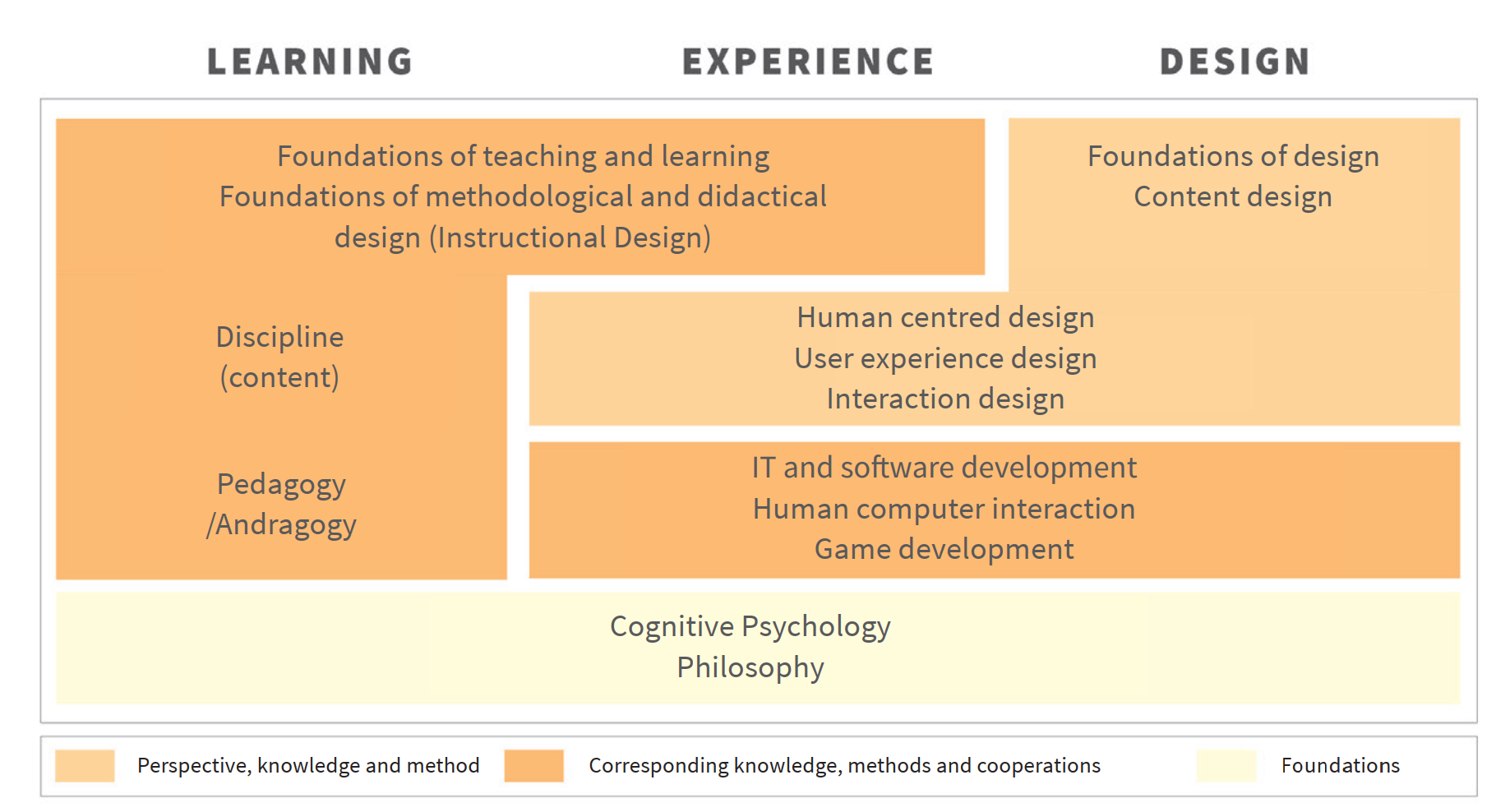
This type of design applies design methods and knowledge and employs suitable modern technologies. LXD thus combines specific design expertise with knowledge and experience from the field of instructional design. Among others, design knowledge and methods
are drawn from the fields of interaction design, user experience design and graphic design. Furthermore, close collaboration with colleagues from disciplines such as IT and application development is required. In the next sections, the terms Experience, Learning and Design will be explained in more detail.
Learning Experience Design (LXD) is a combination of the terms Learning (L), Experience (X) and Design (D) and is concerned with the creation of engaging learning experiences.
Experience

The term experience derives from the understanding in user experience design. The focus lies on the learners and on what they experience. Here, the design perspective plays a central role. It is about about how learners are doing in their learning, so it is not a matter of designing the direct interaction with a learning tool (e.g. what colour a button has), but rather of grasping and designing the entire learning context of the learners.
Design
Principles and procedures from various design disciplines are used to shape the learning experience. It is a creative process that constantly seeks to work in a design-innovative way in order to generate the best possible ideas, designs and solutions.
Learning
The experience we design is attributed to learning. Training, teaching or instructing are not at the centre of attention. Rather, the focus is on the learners, their environment and learning experience. In some publications, the term ”experiential learning“ is also used.
more about me in the FAQ.
LXD from a design perspective
Designers have discovered the field of LXD as a design discipline for themselves. In this field, they apply their design knowledge and methods. The focus of designers is on human beings, i.e. the learners, and they become the centre of the work. Furthermore, LXD as a design discipline focuses more on the functional than the aesthetic aspects (as in industrial design, for example).
LXD from a teacher's perspective
Teachers are always oriented towards people, i.e. towards the learner. As their focus is on learning and teaching, the designer‘s point of view can seem odd to teachers at first. Nonetheless, the use of design procedures and methods is both exciting and helpful for teachers as well as developers of technology-enhanced learning applications.
Challenges of LXD
LXD is a relatively new design discipline. Since the terminology has not been clearly defined yet, it is not yet clear which foundations LXD actually needs. The design process of technology-enhanced learning experiences requires specific specialisations and produces corresponding results; therefore, LXD designers cannot be responsible for the whole process. As a result, close collaboration with other disciplines is required.
Different understanding of terminology
LXD in detail is viewed quite diversely. The team of Educational Technology (LLT), like many others, recognises LXD as a new design discipline. The word ”design“ is used very broadly in the English-speaking world, which can lead to misunderstandings. Didactic design or instructional design also have little in common with traditional design disciplines such as graphic design, architecture or industrial design. Even though the tools, work practices, expectations, methods and approaches of the two groups differ, LXD requires them to work together.
Conclusion - LXD at TU Graz
The aim of LXD is to create learning environments that are as intuitive, engaging and easy to use as possible. The pedagogical and didactical preparation as well as the technical implementation of digital learning experiences are no less significant than the creative processes and the final design of LXD. Modern teaching and learning environments not only require interdisciplinary teams, but also staff specialised in this design discipline. LXD is essential for designing and implementing technology-enhanced learning and teaching in a way that enhances the experiences of students and teachers. The organisational unit Educational Technology (LLT) expands the knowledge of the design team on LXD to further enrich the teaching and learning experience at TU Graz.

Sources and tips for further reading:
Ahn, J. (2019): Drawing Inspiration for Learning Experience Design (LX) from Diverse Perspectives. In: The Emerging Learning Design Journal, 2019, Vol. 6, Iss. 1, Article 1.
Schmidt, M./Tawfik, A. A./Jahnke, I./Earnshaw, Y. (2020): Learner and User Experience Research. An Introduction for the Field of LearningDesign & Technology. EdTech Books.
LXD.org (2021b): What is learning experience design? (Webpage)
LXD.org (2021a): The origin of learning experience design (Webpage)
Ebner, Martin, Schön, Sandra, Kircher, Jacqueline & Burger, Eva-Maria (2021). Learning Experience Design: Zur Gestaltung von technologiegestützten Lernerfahrungen mit Methoden der Design-Entwicklung. Handbuch E-Learning. Erg. Lfg. In Print. (available in German)
 TU Graz Educational Technology
TU Graz Educational Technology